Fever and swollen extremities in a 3-week-old
A 3-week-old baby boy is brought to the emergency depratment with swelling of hands and feet. His extremities were edematous, erythematous, and appeared painful.
The Case
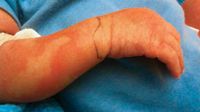
Diagnosis: Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (AHEI) is a benign, cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis typically seen in children younger than 2 years of age. It is characterized by mild fever and purpuric, edematous lesions on the face, scrotal region, and extremities.1 Lesions on the trunk and significant systemic symptoms are generally not present, although cases of articular involvement, such as joint pain and swelling, and bacteremia have been reported.2,3
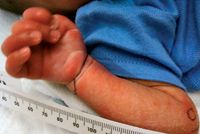
Onset may be sudden and dramatic. Laboratory tests are not typically diagnostic, although leukocytosis, elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and thrombocytosis may be found. Histopathology demonstrates leukocytoclastic vasculitis of the dermal vessels and fibrinoid necrosis; occasionally, immune complexes, particularly fibrinogen, C3, IgG, IgM, IgA, and IgE, can be detected in the walls of and around small vessels.4
Recognize & Refer: Hemangiomas in pediatrics
July 17th 2019Contemporary Pediatrics sits down exclusively with Sheila Fallon Friedlander, MD, a professor dermatology and pediatrics, to discuss the one key condition for which she believes community pediatricians should be especially aware-hemangiomas.